老師講了一個觀念我覺得很不錯,Asympotic 也就是漸進線的意思,當 n 夠大時,會趨近某值。而 Big-O 也就是當 input size 夠大時,係數的差異就可以忽略過去。
這五種 asymptotic notation 之前就學過了,所以上課就比較沒有認真聽,不過再聽一次 Big-O 的定義時,覺得這種定義就很自然。
因為教科書上的定義問題,老師有解釋了一下,因為 computer 是離散的,但用連續函數表示比較方便,為了方便表示或是分析,有時候 n 會允許負數,雖然現實上是不可能。就方便方便~
關於定義的部分就參考講義,這裡要注意的是 Big-O 的定義和 Little-o 定義的差別,Big-O 是存在一個 c 而 Little-o 則是對每一個 c。
跟微積分一樣,證明極限值若用定義方式證明很不容易,像是扯到對數的話,這裡提供一個定理,接下來證明的話,可以用上下微分的方式來求出值...
懂概念就好,這證明也很簡單,兩邊的定義寫一下,就可以看出來相等。主要還是 O o 大於小於的觀念。
2011年2月28日 星期一
[Introduction To Algorithms] 第一堂: Getting Started (3)
上一堂課說明 profile script 的寫法時,因為快下課了,所以講的很急,也有點亂,課堂一開始先把這個部分在說明一下。上一個 blog 最後一張圖,有說明我就不重複貼了
- -b brief mode (不要有過多的資訊, cumulative 會重複)
- gprof a.out a.out.gomn (原本打 gprof 就可以了,但因為這學期系記中 server 重灌,所以有些設定不一樣....)
 接下來說明如何分析 insertion sort 的係數
接下來說明如何分析 insertion sort 的係數 接 insertion sort 分析完後,再分析 merge sort 的係數, merge sort 的係數比較難分析,牽扯到對數。可能要用查表或是數值方法來算出值來。
作業一就是要寫改良版的 insert sort 和 merge sort 並用 gprof 估算時間。
insert sort 的改良方式是用 binary search 替代 sequential 找出該插入的點。
merge 則是用取消 copy back 的版本
作業一寫出來後,可以拿改良的版本跟 STL 的sort 做比較,應該是蠻有趣的 XD
哼哼
標籤:
Algorithm
2011年2月24日 星期四
[Introduction To Algorithms] 第一堂: Getting Started (2)
延續上個問題
- 為什麼 c 和 cn 使用的是同樣的 c ?
書上的說法是 c 取上界,取下界算出來的答案都是 nlg n。
而到了 chapter 4 時有個理論可以說明即使都用 c 還是沒差 (印象中好像是 master theorem = =)
老師補充了他自己的證明,不一樣的�nnlg�nn變常數變
就用不一樣的常數變數表示。這樣證明比較簡單,不用用三明治的方式上下夾擊。
接下來比較 insertion 和 merge sort 的係數。
因為 merge 需要漲堆疊、而且要 copy array 所以係數會比較高。因此若是 input size 很小時,insertion sort 會比較快。但是要小到甚麼程度呢?
這就要看執行環境了...
Note:
- 估算空間複雜度時,是估算額外用到的空間,原本的空間是本來就要用的。
- 所以排序要比較快,就是用混用的方法,一開始遞迴呼叫 merge sort 等到 input size 夠小時,呼叫 insertion sort
這裡用 shell script 來 filter 不需要的資訊
- A2 指的是保留兩列
就降!
標籤:
Algorithm
2011年2月23日 星期三
[More iPhone SDK 心得] Chap4 The Devil in the Detail View
 |
| 主畫面 |
 |
| Table-Based Detail View |
Note: > 英文叫做 disclosure indicator
而 Detail View 設計的困難在於其對應關係,例如我按下 Name 這個 cell 、或是按下 Birthdate cell,會有不同的 Editing SubController 產生,要如何設計其對應關係, that's a challenge。
下面的 code 是一般的做法,這種 nested switch 的方式造成 maintain 上的困難,本章是結合 paired array 和 nested array 的方式來處理對應關係,有彈性的多。
enum HeroEditControllerSections {HeroEditControllerSectionName = 0,HeroEditControllerSectionGeneral,HeroEditControllerSectionCount};enum HeroEditControllerNameSection {HeroEditControllerNameRow = 0,HeroEditControllerNameSectionCount};enum HeroEditControllerGeneralSection {HeroEditControllerGeneralSectionSecretIdentityRow,HeroEditControllerGeneralSectionBirthdateRow,HeroEditControllerGeneralSectionSexRow,HeroEditControllerGeneralSectionCount};//Then, in every method where you are provided with an index path, you can take the//appropriate action based on the row and section represented by the index path, using//switch statements, like this:- (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableViewdidSelectRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath {NSUInteger section = [indexPath section];NSUInteger row = [indexPath row];switch (section) {case HeroEditControllerSectionName:switch (row){case HeroEditControllerNameRow :// Create a controller to edit name// and push it on the stack...break;default:break;}break;case HeroEditControllerSectionGeneral:switch (row) {case HeroEditControllerGeneralSectionSecretIdentityRow:// Create a controller to edit secret identity// and push it on the stack...CHAPTER 4: The Devil in the Detail View 87break;case HeroEditControllerGeneralSectionBirthdateRow:// Create a controller to edit birthdate and// push it on the stack...break;case HeroEditControllerGeneralSectionSexRow:// Create a controller to edit sex and push it// on the stack...break;default:break;}break;default:break;}}
// combine nested and paired array
- (void)viewDidLoad {sectionNames = [[NSArray alloc] initWithObjects:[NSNull null],NSLocalizedString(@"General", @"General"),nil];rowLabels = [[NSArray alloc] initWithObjects:// Section 1[NSArray arrayWithObjects:NSLocalizedString(@"Name", @"Name"), nil],// Section 2[NSArray arrayWithObjects:NSLocalizedString(@"Identity", @"Identity"),NSLocalizedString(@"Birthdate", @"Birthdate"),NSLocalizedString(@"Sex", @"Sex"),nil],// Sentinelnil];rowKeys = [[NSArray alloc] initWithObjects:// Section 1[NSArray arrayWithObjects:@"name", nil],// Section 2[NSArray arrayWithObjects:@"secretIdentity", @"birthdate", @"sex", nil],// Sentinelnil];rowControllers = [[NSArray alloc] initWithObjects:// Section 1[NSArray arrayWithObject:@"ManagedObjectStringEditor"],// Section 2[NSArray arrayWithObjects:@"ManagedObjectStringEditor",@"ManagedObjectDateEditor",@"ManagedObjectSingleSelectionListEditor", nil],// Sentinelnil];rowArguments = [[NSArray alloc] initWithObjects:// Section 1[NSArray arrayWithObject:[NSNull null]],// Section 2,[NSArray arrayWithObjects:[NSNull null],[NSNull null],[NSDictionary dictionaryWithObject:[NSArrayarrayWithObjects:@"Male", @"Female", nil]forKey:@"list"],nil],// Sentinelnil];[super viewDidLoad];}
這裡有用到 [NSNull null]] 到的技巧,第一次看不是很明白,主要是用於 unname section 的情況??
接下來是設計真正的 editing subcontroller 的部份,下面兩張圖分別是 Birthdate 和 Name 欄位的editing subcontroller,這裡用了相同的父類別 (終於用到繼承了 XD) 來提取相同的部份。
對於 attribute 的字串處理 ,用到了 category 的技巧,如下 code
@protocol HeroValueDisplay- (NSString *)heroValueDisplay;@end@interface NSString (HeroValueDisplay)- (NSString *)heroValueDisplay;@end@interface NSDate (HeroValueDisplay)- (NSString *)heroValueDisplay;@end@interface NSNumber (HeroValueDisplay)- (NSString *)heroValueDisplay;@end@interface NSDecimalNumber (HeroValueDisplay)- (NSString *)heroValueDisplay;@end
其他要注意的是
- loadview 的使用時機 (在 datapicker 中有用到)
- UIButton 和 Bar Button 之間的不同
- NSClassFromString 的使用技巧 (like Java's Introspection)
這章很多東西 = =

hi
標籤:
iPhone
2011年2月22日 星期二
[More iPhone SDK 心得] Chap3 A Super Start:Adding,Displaying,and Deleting Data
本章實作了一個簡單的 Core Data "Hero" 然後利用 Table View 來顯示
而 Tab Bar 則是控制 Hero 的排序方式

這裡要注意的是 name 和 secretIdentity 都是必須的欄位
所以 optional 要uncheck 並給預設值 (我忘記給預設值所以當了很多次)
這裡跟 paparazzi 2 的地方不同
需要思考的是 MainWindow 的 root controller
是什麼 Tab Bar or Navigation View Controller
在這裡是用 Navigation Controller 因為這兩個Tab Item 都是存取同一個 Table View
這個範例用陽春的 window-based with core data 去 expand 因此把所有的控制邏輯都寫到 HeroListViewController 上
像是 UITableViewDelegate UITableViewDataSource UITabBarDelegate UIAlertViewDelegate NSFetchedResultsControllerDelegate
等這些都要自己實作
其他就是 code 撰寫的部份 比較不熟的部份還是 fetchResultsController 的部份
書上的 navigation core data-based template 和我現在的 Xcode 產生出來的似乎不一樣
這裡有個小訣竅關於註解的
而 Tab Bar 則是控制 Hero 的排序方式

這裡要注意的是 name 和 secretIdentity 都是必須的欄位
所以 optional 要uncheck 並給預設值 (我忘記給預設值所以當了很多次)
這裡跟 paparazzi 2 的地方不同
需要思考的是 MainWindow 的 root controller
是什麼 Tab Bar or Navigation View Controller
在這裡是用 Navigation Controller 因為這兩個Tab Item 都是存取同一個 Table View
這個範例用陽春的 window-based with core data 去 expand 因此把所有的控制邏輯都寫到 HeroListViewController 上
像是 UITableViewDelegate UITableViewDataSource UITabBarDelegate UIAlertViewDelegate NSFetchedResultsControllerDelegate
等這些都要自己實作
其他就是 code 撰寫的部份 比較不熟的部份還是 fetchResultsController 的部份
書上的 navigation core data-based template 和我現在的 Xcode 產生出來的似乎不一樣
這裡有個小訣竅關於註解的
標籤:
iPhone
2011年2月21日 星期一
[Introduction To Algorithms] 第一堂: Getting Started
 |
| http://mitpress.mit.edu/algorithms/ |
之前看過幾遍,寫的很好,
得過很多獎項。
而要測量演算法的 performance 時,需要考慮演算法的執行環境- computation model。這本書的 model 是 RAM (single process random-access machine) 。而若是跑在multi-process computation model 下,評估的方式就不一樣了。
一個演算法要餵資料給它執行,而執行的時間跟輸入資料的大小有關 - input size。要注意的是並不是每個演算法的 input size 都一樣,老師有提到像是 insertion sort 的 input size 和 prime 的 input size 不一樣。
insertion sort : the number of elements being sorted
prime: the number of bits
若是 prime 以 insertion sort 方式估計 performance 為 O(N .5) 但實際上它是指數的方式遞增。
這讓人有些混淆,課程最後講到 Hard Program 時會比較清楚。
分析一個演算法的 performance 有三種 case :
best case: 算好玩的而已。
average case: 通常 average 會向 worst case 靠 (老師逗了一個哏: 人生不如意之事,十之八九)
worst case: 最重要。
而評估 average case 最難,因為要靠機率來分析,教科書上會有蠻多例子來分析 average case....
分析演算法時並不是每個指令都要分析,找出執行次數最多的指令分析即可 -- basic operation
以迴圈來講,就找出巢狀迴圈的最內層分析就對了。
接下來就分析了 insertion sort 的 performance、開始講 merge sort,
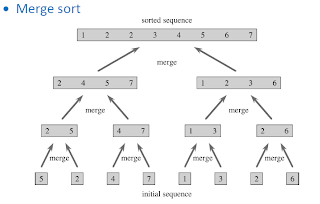 |
| Merge Sort 示意圖 |
分析 Merge Sort 時,有幾項困難,首先假設input size 是 2 的 次方,這樣就可以用 recursion tree 的方式做估算
這裡要注意的是, 2*T(n/2) 這個式子,是把 n 當作連續來處理,而 computer science 是離散的,正確寫法是 T(Floor n/2) + T(Ceiling n/2),為什麼用連續的方式寫ok ,以及 c 和 2T(n/2)+cn 中這裡個 c 不是同樣的東西,怎麼可以都用 c 來表赤。
這就是下一堂課要介紹的了。
舒服!!
標籤:
Algorithm
[Distributed Algorithms] 第一堂: Introduction
這門課是偏理論的課,原本以為會跟實作相關,像是講解 Java RMI 之類的課。
老師說基本上都是定義與證明。 也好,最近都在寫 code 很少碰理論的東西了。
使用的教科書: MIT 教授寫的,相當學院派
Distributed algorithms, by Nancy Lynch, Morgan Kaufmann, 1996
首先說明與平行演算法的不同,基本上平行演算法的環境比較確定,向分散式演算法就不能假設 processes 的差異。
再來畫了一個樹狀圖說明演算法證明的分類。
老師舉了清大夜市的紅綠燈管理系統
safety:不會出車禍
progress: 保值車輛流通
safety 與 progress 在以後的證明風格會差很多。
因為是第一堂課,所以也就僅止於介紹,老師舉了一些很有趣的例子
1. Muddy Children forehead (google 面試的考題)
2. 莊子的子非魚
3. Coordinated Attack Program
4. 村莊裡的大屠殺
1和4是哲學的思辨,重點在 Know 這個字
3 是 Jim Gray (Turing Award的得主,釣魚的時候失蹤)
下堂課會開始講 OS 的 Mutual Exclusion Algorithm
應該會理論到不行
舒服!
老師說基本上都是定義與證明。 也好,最近都在寫 code 很少碰理論的東西了。
使用的教科書: MIT 教授寫的,相當學院派
Distributed algorithms, by Nancy Lynch, Morgan Kaufmann, 1996
首先說明與平行演算法的不同,基本上平行演算法的環境比較確定,向分散式演算法就不能假設 processes 的差異。
再來畫了一個樹狀圖說明演算法證明的分類。
老師舉了清大夜市的紅綠燈管理系統
safety:不會出車禍
progress: 保值車輛流通
safety 與 progress 在以後的證明風格會差很多。
因為是第一堂課,所以也就僅止於介紹,老師舉了一些很有趣的例子
1. Muddy Children forehead (google 面試的考題)
2. 莊子的子非魚
3. Coordinated Attack Program
4. 村莊裡的大屠殺
1和4是哲學的思辨,重點在 Know 這個字
3 是 Jim Gray (Turing Award的得主,釣魚的時候失蹤)
下堂課會開始講 OS 的 Mutual Exclusion Algorithm
應該會理論到不行
舒服!
標籤:
Algorithm
2011年2月18日 星期五
Property Lists
從 bundle 中讀取 plist 範例:
- (void)viewDidLoad {
NSString *path = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"sortednames" ofType:@"plist"];
NSDictionary *dict = [[NSDictionary alloc] initWithContentsOfFile:path];
[dict release];
}
訂閱:
意見 (Atom)


















